
Additive Markov chain
Encyclopedia
In probability theory
, an additive Markov chain is a Markov chain
with an additive
conditional probability function. Here the process is a discrete-time Markov chain of order m and the transition probability to a state at the next time is a sum of functions, each depending on the next state and one of the m previous states.
s X1, X2, X3, ..., possessing the following property: the probability that a random variable Xn has a certain value xn under the condition that the values of all previous variables are fixed depends on the values of m previous variables only (Markov chain
of order m), and the influence of previous variables on a generated one is additive,
 .
.
of the chain consists on two values only, Xn ∈ { x1, x2 }. For example, Xn ∈ { 0, 1 }. The conditional probability function of a binary additive Markov chain can be represented as
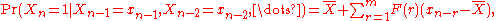
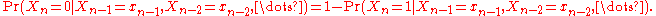
Here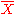 is the probability to find Xn = 1 in the sequence and
is the probability to find Xn = 1 in the sequence and
F(r) is referred to as the memory function. The value of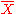 and the function F(r) contain all the information about correlation
and the function F(r) contain all the information about correlation
properties of the Markov chain.
between the variables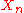 and
and 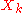 of the chain depends on the distance
of the chain depends on the distance  only. It is defined as follows:
only. It is defined as follows:
where the symbol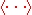 denotes averaging over all n. By definition,
denotes averaging over all n. By definition,
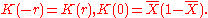
There is a relation between the memory function and the correlation function of the binary additive Markov chain:

Probability theory
Probability theory is the branch of mathematics concerned with analysis of random phenomena. The central objects of probability theory are random variables, stochastic processes, and events: mathematical abstractions of non-deterministic events or measured quantities that may either be single...
, an additive Markov chain is a Markov chain
Markov chain
A Markov chain, named after Andrey Markov, is a mathematical system that undergoes transitions from one state to another, between a finite or countable number of possible states. It is a random process characterized as memoryless: the next state depends only on the current state and not on the...
with an additive
Additive function
In mathematics the term additive function has two different definitions, depending on the specific field of application.In algebra an additive function is a function that preserves the addition operation:for any two elements x and y in the domain. For example, any linear map is additive...
conditional probability function. Here the process is a discrete-time Markov chain of order m and the transition probability to a state at the next time is a sum of functions, each depending on the next state and one of the m previous states.
Definition
An additive Markov chain of order m is a sequence of random variableRandom variable
In probability and statistics, a random variable or stochastic variable is, roughly speaking, a variable whose value results from a measurement on some type of random process. Formally, it is a function from a probability space, typically to the real numbers, which is measurable functionmeasurable...
s X1, X2, X3, ..., possessing the following property: the probability that a random variable Xn has a certain value xn under the condition that the values of all previous variables are fixed depends on the values of m previous variables only (Markov chain
Markov chain
A Markov chain, named after Andrey Markov, is a mathematical system that undergoes transitions from one state to another, between a finite or countable number of possible states. It is a random process characterized as memoryless: the next state depends only on the current state and not on the...
of order m), and the influence of previous variables on a generated one is additive,
 .
.Binary case
A binary additive Markov chain is where the state spaceState space
In the theory of discrete dynamical systems, a state space is a directed graph where each possible state of a dynamical system is represented by a vertex, and there is a directed edge from a to b if and only if ƒ = b where the function f defines the dynamical system.State spaces are...
of the chain consists on two values only, Xn ∈ { x1, x2 }. For example, Xn ∈ { 0, 1 }. The conditional probability function of a binary additive Markov chain can be represented as
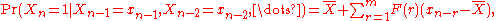
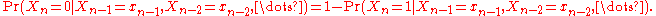
Here
 is the probability to find Xn = 1 in the sequence and
is the probability to find Xn = 1 in the sequence andF(r) is referred to as the memory function. The value of
 and the function F(r) contain all the information about correlation
and the function F(r) contain all the information about correlationCorrelation
In statistics, dependence refers to any statistical relationship between two random variables or two sets of data. Correlation refers to any of a broad class of statistical relationships involving dependence....
properties of the Markov chain.
Relation between the memory function and the correlation function
In the binary case, the correlation functionCorrelation function
A correlation function is the correlation between random variables at two different points in space or time, usually as a function of the spatial or temporal distance between the points...
between the variables
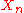 and
and 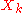 of the chain depends on the distance
of the chain depends on the distance  only. It is defined as follows:
only. It is defined as follows:
where the symbol
 denotes averaging over all n. By definition,
denotes averaging over all n. By definition,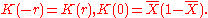
There is a relation between the memory function and the correlation function of the binary additive Markov chain:


