Activated protein C resistance
Encyclopedia
Activated protein C resistance is a hemostatic disorder
characterized by a poor anticoagulant
response to activated protein C
(APC). This results in an increased risk of venous thrombosis
, which can cause heart attacks
, stroke
s, and other problems with circulation.
The disorder can be acquired or inherited, the hereditary form having an autosomal dominant inheritance pattern.
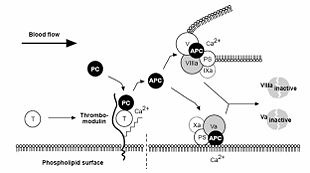 Activated protein C (with protein S as a cofactor) degrades Factor V
Activated protein C (with protein S as a cofactor) degrades Factor V
a and Factor VIII
a. Activated protein C resistance is the inability of protein C to cleave Factor V
a and/or Factor VIII
a, which allows for longer duration of thrombin generation and may lead to a hypercoagulable state. This may be hereditary or acquired. The best known and most common hereditary form is Factor V Leiden
. Acquired forms occur in the presence of elevated Factor VIII concentrations.
Hemostasis
Hemostasis or haemostasis is a process which causes bleeding to stop, meaning to keep blood within a damaged blood vessel . Most of the time this includes blood changing from a liquid to a solid state. Intact blood vessels are central to moderating blood's tendency to clot...
characterized by a poor anticoagulant
Anticoagulant
An anticoagulant is a substance that prevents coagulation of blood. A group of pharmaceuticals called anticoagulants can be used in vivo as a medication for thrombotic disorders. Some anticoagulants are used in medical equipment, such as test tubes, blood transfusion bags, and renal dialysis...
response to activated protein C
Protein C
Protein C, also known as autoprothrombin IIA and blood coagulation factor XIV, is a zymogenic protein, the activated form of which plays an important role in regulating blood clotting, inflammation, cell death and maintaining the permeability of blood vessel walls in humans and other animals...
(APC). This results in an increased risk of venous thrombosis
Venous thrombosis
A venous thrombosis is a blood clot that forms within a vein. A venous thrombosis is a blood clot that forms within a vein. A venous thrombosis is a blood clot that forms within a vein. (Thrombosis is a medical term for blood clotting (Haemostasis) occurring in the wrong place, i.e...
, which can cause heart attacks
Myocardial infarction
Myocardial infarction or acute myocardial infarction , commonly known as a heart attack, results from the interruption of blood supply to a part of the heart, causing heart cells to die...
, stroke
Stroke
A stroke, previously known medically as a cerebrovascular accident , is the rapidly developing loss of brain function due to disturbance in the blood supply to the brain. This can be due to ischemia caused by blockage , or a hemorrhage...
s, and other problems with circulation.
The disorder can be acquired or inherited, the hereditary form having an autosomal dominant inheritance pattern.
Pathophysiology

Factor V
Factor V is a protein of the coagulation system, rarely referred to as proaccelerin or labile factor. In contrast to most other coagulation factors, it is not enzymatically active but functions as a cofactor...
a and Factor VIII
Factor VIII
Factor VIII is an essential blood clotting factor also known as anti-hemophilic factor . In humans, Factor VIII is encoded by the F8 gene...
a. Activated protein C resistance is the inability of protein C to cleave Factor V
Factor V
Factor V is a protein of the coagulation system, rarely referred to as proaccelerin or labile factor. In contrast to most other coagulation factors, it is not enzymatically active but functions as a cofactor...
a and/or Factor VIII
Factor VIII
Factor VIII is an essential blood clotting factor also known as anti-hemophilic factor . In humans, Factor VIII is encoded by the F8 gene...
a, which allows for longer duration of thrombin generation and may lead to a hypercoagulable state. This may be hereditary or acquired. The best known and most common hereditary form is Factor V Leiden
Factor V Leiden
Factor V Leiden is the name given to a variant of human factor V that causes a hypercoagulability disorder. In this disorder the Leiden variant of factor V cannot be inactivated by activated protein C. Factor V Leiden is the most common hereditary hypercoagulability disorder amongst Eurasians...
. Acquired forms occur in the presence of elevated Factor VIII concentrations.

