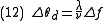Acousto-Optic Deflector
Encyclopedia
An acousto-optic deflector spatially controls the optical beam. In the operation of an acousto-optic deflector the power driving the acoustic transducer is kept on, at a constant level, while the acoustic frequency is varied to deflect the beam to different angular positions. The acousto-optic deflector makes use of the acoustic frequency dependent diffraction angle, where a change in the angle 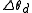 as a function of the change in frequency
as a function of the change in frequency 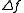 given as,
given as,
where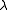 is the optical wavelength and
is the optical wavelength and  is the velocity of the acoustic wave.
is the velocity of the acoustic wave.
AOD technology has made practical the Bose-Einstein condensation for which the 2001 Nobel Prize in Physics
was awarded to Eric A. Cornell, Wolfgang Ketterle
and Carl E. Wieman. Another application of acoustic-optical deflection is optical trapping of small molecules.
AODs are essentially the same as acousto-optic modulator
s (AOMs). In an AOM, only the amplitude of the sound wave is modulated (to modulate the intensity of the diffracted laser beam), whereas in an AOD, both the amplitude and frequency are adjusted, making the engineering requirements tighter for an AOD than an AOM.
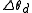 as a function of the change in frequency
as a function of the change in frequency 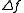 given as,
given as,where
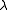 is the optical wavelength and
is the optical wavelength and  is the velocity of the acoustic wave.
is the velocity of the acoustic wave.AOD technology has made practical the Bose-Einstein condensation for which the 2001 Nobel Prize in Physics
Nobel Prize in Physics
The Nobel Prize in Physics is awarded once a year by the Royal Swedish Academy of Sciences. It is one of the five Nobel Prizes established by the will of Alfred Nobel in 1895 and awarded since 1901; the others are the Nobel Prize in Chemistry, Nobel Prize in Literature, Nobel Peace Prize, and...
was awarded to Eric A. Cornell, Wolfgang Ketterle
Wolfgang Ketterle
Wolfgang Ketterle is a German physicist and professor of physics at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology . His research has focused on experiments that trap and cool atoms to temperatures close to absolute zero, and he led one of the first groups to realize Bose-Einstein condensation in these...
and Carl E. Wieman. Another application of acoustic-optical deflection is optical trapping of small molecules.
AODs are essentially the same as acousto-optic modulator
Acousto-optic modulator
An acousto-optic modulator , also called a Bragg cell, uses the acousto-optic effect to diffract and shift the frequency of light using sound waves . They are used in lasers for Q-switching, telecommunications for signal modulation, and in spectroscopy for frequency control. A piezoelectric...
s (AOMs). In an AOM, only the amplitude of the sound wave is modulated (to modulate the intensity of the diffracted laser beam), whereas in an AOD, both the amplitude and frequency are adjusted, making the engineering requirements tighter for an AOD than an AOM.
See also
- Acousto-optic modulatorAcousto-optic modulatorAn acousto-optic modulator , also called a Bragg cell, uses the acousto-optic effect to diffract and shift the frequency of light using sound waves . They are used in lasers for Q-switching, telecommunications for signal modulation, and in spectroscopy for frequency control. A piezoelectric...
- Acousto-opticsAcousto-opticsAcousto-optics is a branch of physics that studies the interactions between sound waves and light waves, especially the diffraction of laser light by ultrasound or sound in general.-Introduction:...
- Nonlinear opticsNonlinear opticsNonlinear optics is the branch of optics that describes the behavior of light in nonlinear media, that is, media in which the dielectric polarization P responds nonlinearly to the electric field E of the light...
- SonoluminescenceSonoluminescenceSonoluminescence is the emission of short bursts of light from imploding bubbles in a liquid when excited by sound.-History:The effect was first discovered at the University of Cologne in 1934 as a result of work on sonar. H. Frenzel and H. Schultes put an ultrasound transducer in a tank of...