
APXS
Encyclopedia

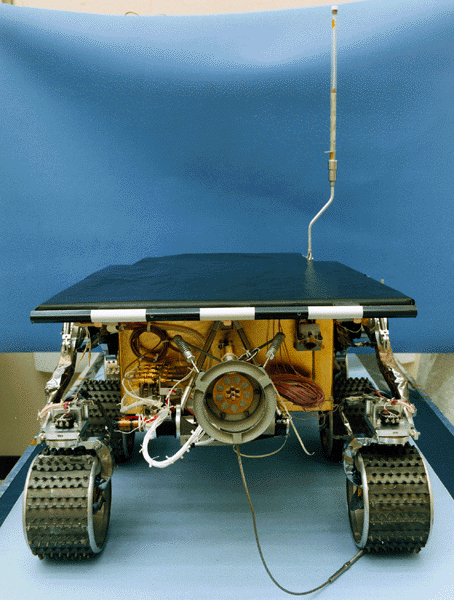
Mars Pathfinder
Mars Pathfinder was an American spacecraft that landed a base station with roving probe on Mars in 1997. It consisted of a lander, renamed the Carl Sagan Memorial Station, and a lightweight wheeled robotic rover named Sojourner.Launched on December 4, 1996 by NASA aboard a Delta II booster a...
) is a device that analyses the chemical element composition of a sample from the scattered alpha particle
Alpha particle
Alpha particles consist of two protons and two neutrons bound together into a particle identical to a helium nucleus, which is classically produced in the process of alpha decay, but may be produced also in other ways and given the same name...
s, emitted protons (for Pathfinder only), and fluorescent X-ray
X-ray
X-radiation is a form of electromagnetic radiation. X-rays have a wavelength in the range of 0.01 to 10 nanometers, corresponding to frequencies in the range 30 petahertz to 30 exahertz and energies in the range 120 eV to 120 keV. They are shorter in wavelength than UV rays and longer than gamma...
s after the sample is irradiated with alpha particles and X-rays from radioactive sources. Since there are faster methods available which do not use radioactive material to analyse the elemental composition of a sample, this compact and low power method is most often used on space missions.
Over the years several modified versions of the APS (without X-ray spectrometer) or APXS have been flown: Surveyor 5-7
Surveyor program
The Surveyor Program was a NASA program that, from 1966 through 1968, sent seven robotic spacecraft to the surface of the Moon. Its primary goal was to demonstrate the feasibility of soft landings on the Moon...
, Mars Pathfinder
Mars Pathfinder
Mars Pathfinder was an American spacecraft that landed a base station with roving probe on Mars in 1997. It consisted of a lander, renamed the Carl Sagan Memorial Station, and a lightweight wheeled robotic rover named Sojourner.Launched on December 4, 1996 by NASA aboard a Delta II booster a...
, Mars 96
Mars 96
Mars 96 was a failed Mars mission launched in 1996 to investigate Mars by the Russian Space Forces and not directly related to the Soviet Mars probe program of the same name. After failure of the second fourth-stage burn, the probe assembly re-entered the Earth's atmosphere, breaking up over a...
, Mars Exploration Rover
Mars Exploration Rover
NASA's Mars Exploration Rover Mission is an ongoing robotic space mission involving two rovers, Spirit and Opportunity, exploring the planet Mars...
, Phobos.
Phobos program
The Phobos program was an unmanned space mission consisting of two probes launched by the Soviet Union to study Mars and its moons Phobos and Deimos. Phobos 2 became a Mars orbiter and returned 38 images with a resolution of up to 40 meters...
APS devices will be included on several upcoming missions:
Rosetta/Philae
Philae lander
Philae is the lander that accompanies the Rosetta spacecraft. It is designed to land on Comet 67P/Churyumov-Gerasimenko shortly after arrival...
, Mars Science Laboratory
Mars Science Laboratory
The Mars Science Laboratory is a National Aeronautics and Space Administration mission with the aim to land and operate a rover named Curiosity on the surface of Mars. The MSL was launched November 26, 2011, at 10:02 EST and is scheduled to land on Mars at Gale Crater between August 6 and 20, 2012...
and Exomars
ExoMars
ExoMars is a European-led robotic mission to Mars currently under development by the European Space Agency with collaboration by NASA...
missions.
Source
Several forms of radiation are used in APXS. They include alpha particles, protons, and X-rays. Alpha particles, protons, and X-rays are emitted during the radioactive decay of unstable atoms. A common source of alpha particles is curiumCurium
Curium is a synthetic chemical element with the symbol Cm and atomic number 96. This radioactive transuranic element of the actinide series was named after Marie Skłodowska-Curie and her husband Pierre Curie. Curium was first intentionally produced and identified in summer 1944 by the group of...
244. It emits particles with an energy of 5.8 MeV
MEV
MeV and meV are multiples and submultiples of the electron volt unit referring to 1,000,000 eV and 0.001 eV, respectively.Mev or MEV may refer to:In entertainment:* Musica Elettronica Viva, an Italian musical group...
. X-rays of 14 and 18 keV are emitted in the decay of plutonium
Plutonium
Plutonium is a transuranic radioactive chemical element with the chemical symbol Pu and atomic number 94. It is an actinide metal of silvery-gray appearance that tarnishes when exposed to air, forming a dull coating when oxidized. The element normally exhibits six allotropes and four oxidation...
240. The Mars Exploration Rover
Mars Exploration Rover
NASA's Mars Exploration Rover Mission is an ongoing robotic space mission involving two rovers, Spirit and Opportunity, exploring the planet Mars...
s' Athena payload uses curium
Curium
Curium is a synthetic chemical element with the symbol Cm and atomic number 96. This radioactive transuranic element of the actinide series was named after Marie Skłodowska-Curie and her husband Pierre Curie. Curium was first intentionally produced and identified in summer 1944 by the group of...
244 witth a source strength of approximately 30 mCi.
Alpha particles
Some of the alpha particles of a defined energy are backscattered to the detector if they collide with an atomic nucleus. The physical laws for Rutherford backscattering in an angle close to 180° are conservation of energyConservation of energy
The nineteenth century law of conservation of energy is a law of physics. It states that the total amount of energy in an isolated system remains constant over time. The total energy is said to be conserved over time...
and conservation of linear momentum. This makes it possible to calculate the mass of the nucleus hit by the alpha particle. Light elements absorb more energy of the alpha particle, while alpha particles are reflected by heavy nuclei nearly with the same energy. The energy spectrum of the scattered alpha particle shows peaks from 25% up to nearly 100% of the initial alpha particles. This spectrum makes it possible to determine the composition of the sample, especially for the lighter elements. The low backscattering rate makes it necessary for elongated irradiation, approx 10 hours.
Protons
Some of the alpha particles are absorbed by the atomic nuclei. The [alpha,proton] process produces protons of a defined energy which are detected. SodiumSodium
Sodium is a chemical element with the symbol Na and atomic number 11. It is a soft, silvery-white, highly reactive metal and is a member of the alkali metals; its only stable isotope is 23Na. It is an abundant element that exists in numerous minerals, most commonly as sodium chloride...
, magnesium
Magnesium
Magnesium is a chemical element with the symbol Mg, atomic number 12, and common oxidation number +2. It is an alkaline earth metal and the eighth most abundant element in the Earth's crust and ninth in the known universe as a whole...
, silicon
Silicon
Silicon is a chemical element with the symbol Si and atomic number 14. A tetravalent metalloid, it is less reactive than its chemical analog carbon, the nonmetal directly above it in the periodic table, but more reactive than germanium, the metalloid directly below it in the table...
, aluminium
Aluminium
Aluminium or aluminum is a silvery white member of the boron group of chemical elements. It has the symbol Al, and its atomic number is 13. It is not soluble in water under normal circumstances....
and sulfur
Sulfur
Sulfur or sulphur is the chemical element with atomic number 16. In the periodic table it is represented by the symbol S. It is an abundant, multivalent non-metal. Under normal conditions, sulfur atoms form cyclic octatomic molecules with chemical formula S8. Elemental sulfur is a bright yellow...
can be detected by this method. This method was only used in the Mars Pathfinder APXS. For the Mars Exploration Rover
Mars Exploration Rover
NASA's Mars Exploration Rover Mission is an ongoing robotic space mission involving two rovers, Spirit and Opportunity, exploring the planet Mars...
s the proton detector was replaced by a second alpha particle sensor.

