3D radar
Encyclopedia
3D radar provides for radar
coverage on three dimensions unlike the more common 2D radar. While the normal 2D radar provides range and azimuth, the 3D radar provides elevation information with range and azimuth. Applications include weather forecasting
, defense and surveillance.
phased-array radar employed by the Ticonderoga class
of guided missile cruisers and other ships so equipped with the Aegis Combat System
.
Stacked beam radars emit and/or receive multiple beams of radio waves at two or more elevation angles. By comparing the relative strengths of the returns from each beam, the elevation of the target can be deduced. An example of a stacked beam radar is the ARSR-4.
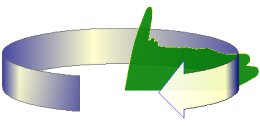
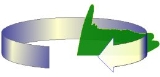
Figure 1: Diagram of a typical 2D radar rotating cosecant squared antenna pattern
Figure 2: Diagram of a typical 3D radar, a judicial mix of vertical electronic beam steering and mechanically horizontal movement of a pencil-beam
Radar
Radar is an object-detection system which uses radio waves to determine the range, altitude, direction, or speed of objects. It can be used to detect aircraft, ships, spacecraft, guided missiles, motor vehicles, weather formations, and terrain. The radar dish or antenna transmits pulses of radio...
coverage on three dimensions unlike the more common 2D radar. While the normal 2D radar provides range and azimuth, the 3D radar provides elevation information with range and azimuth. Applications include weather forecasting
Weather forecasting
Weather forecasting is the application of science and technology to predict the state of the atmosphere for a given location. Human beings have attempted to predict the weather informally for millennia, and formally since the nineteenth century...
, defense and surveillance.
3D radar techniques
Steered beam radars steer a narrow beam through a scan pattern to build a 3-D picture. Examples include NEXRAD doppler weather radar (which uses a parabolic dish) and the AN/SPY-1AN/SPY-1
The AN/SPY-1 is a US naval radar system manufactured by Lockheed Martin. The array is a passive electronically scanned system and is a key component of the Aegis Combat System. The system is computer controlled, using four complementary antennas to provide 360 degree coverage...
phased-array radar employed by the Ticonderoga class
Ticonderoga class cruiser
The Ticonderoga class of missile cruisers is a class of warships in the United States Navy, first ordered and authorized in FY 1978. The class uses phased-array radar and was originally planned as a class of destroyers...
of guided missile cruisers and other ships so equipped with the Aegis Combat System
Aegis combat system
The Aegis Combat System is an integrated naval weapons system developed by the Missile and Surface Radar Division of RCA, and now produced by Lockheed Martin...
.
Stacked beam radars emit and/or receive multiple beams of radio waves at two or more elevation angles. By comparing the relative strengths of the returns from each beam, the elevation of the target can be deduced. An example of a stacked beam radar is the ARSR-4.

Figure 1: Diagram of a typical 2D radar rotating cosecant squared antenna pattern
Figure 2: Diagram of a typical 3D radar, a judicial mix of vertical electronic beam steering and mechanically horizontal movement of a pencil-beam

