
11Beta Hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase
Encyclopedia
11β-Hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase (HSD-11β or 11β-HSD) is the name of a family of enzyme
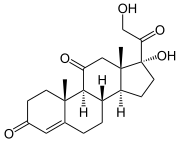
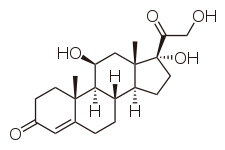
s that catalyze the conversion of inert 11 keto-products (cortisone
) to active cortisol
, or vice versa, thus regulating the access of glucocorticoid
s to the steroid receptors.
, which contains glycyrrhetinic acid
, can inhibit 11β-HSD and lead to a mineralocorticoid excess syndrome.
Inhibition of HSD11B1 has been suggested as a possible therapy for treatment of obesity
and metabolic syndrome
.
Enzyme
Enzymes are proteins that catalyze chemical reactions. In enzymatic reactions, the molecules at the beginning of the process, called substrates, are converted into different molecules, called products. Almost all chemical reactions in a biological cell need enzymes in order to occur at rates...
s that catalyze the conversion of inert 11 keto-products (cortisone
Cortisone
Cortisone is a steroid hormone. It is one of the main hormones released by the adrenal gland in response to stress. In chemical structure, it is a corticosteroid closely related to corticosterone. It is used to treat a variety of ailments and can be administered intravenously, orally,...
) to active cortisol
Cortisol
Cortisol is a steroid hormone, more specifically a glucocorticoid, produced by the adrenal gland. It is released in response to stress and a low level of blood glucocorticoids. Its primary functions are to increase blood sugar through gluconeogenesis; suppress the immune system; and aid in fat,...
, or vice versa, thus regulating the access of glucocorticoid
Glucocorticoid
Glucocorticoids are a class of steroid hormones that bind to the glucocorticoid receptor , which is present in almost every vertebrate animal cell...
s to the steroid receptors.


Function
Cortisol, a glucocorticoid, binds the glucocorticoid receptor. However, because of its molecular similarity to aldosterone it is also capable of binding the mineralcorticoid receptor. Both aldosterone and cortisol have a similar affinity for the mineralocorticoid receptor; however, there is vastly more cortisol in circulation than aldosterone. To prevent over-stimulation of the mineralocorticoid receptor by cortisol, HSD-11β converts the biologically active cortisol to the inactive cortisone, which can no longer bind to the mineralocorticoid receptor. HSD-11β co-localizes with intracellular adrenal steroid receptors. Licorice or CarbenoxoloneCarbenoxolone
Carbenoxolone, a synthetic derivative of glycyrrhetinic acid, is a licensed drug for oesophageal ulceration and inflammation. Other uses include treatment of oral and perioral lesions....
, which contains glycyrrhetinic acid
Glycyrrhetinic acid
Glycyrrhetinic acid is a pentacyclic triterpenoid derivative of the beta-amyrin type obtained from the hydrolysis of glycyrrhizic acid, which was obtained from the herb liquorice. It is used in flavoring and it masks the bitter taste of drugs like aloe and quinine. It is effective in the treatment...
, can inhibit 11β-HSD and lead to a mineralocorticoid excess syndrome.
Isoforms
In humans, there are two HSD11B isoforms:| HSD11B1 Protein:HSD11B1 11β-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase type 1 is an NADPH-dependent enzyme highly expressed in key metabolic tissues including liver, adipose tissue, and the central nervous system.... |
NADPH-dependent | Highly expressed in key metabolic tissues including liver Liver The liver is a vital organ present in vertebrates and some other animals. It has a wide range of functions, including detoxification, protein synthesis, and production of biochemicals necessary for digestion... , adipose tissue Adipose tissue In histology, adipose tissue or body fat or fat depot or just fat is loose connective tissue composed of adipocytes. It is technically composed of roughly only 80% fat; fat in its solitary state exists in the liver and muscles. Adipose tissue is derived from lipoblasts... , and the central nervous system Central nervous system The central nervous system is the part of the nervous system that integrates the information that it receives from, and coordinates the activity of, all parts of the bodies of bilaterian animals—that is, all multicellular animals except sponges and radially symmetric animals such as jellyfish... . |
In these tissues, HSD11B1 reduces cortisone to the active hormone cortisol that activates glucocorticoid receptor Glucocorticoid receptor The glucocorticoid receptor also known as NR3C1 is the receptor to which cortisol and other glucocorticoids bind.... s. |
| HSD11B2 Protein:HSD11B2 Corticosteroid 11-β-dehydrogenase isozyme 2 also known as 11-β-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase 2 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the HSD11B2 gene.- Function :... |
NAD Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide, abbreviated NAD, is a coenzyme found in all living cells. The compound is a dinucleotide, since it consists of two nucleotides joined through their phosphate groups. One nucleotide contains an adenine base and the other nicotinamide.In metabolism, NAD is involved... +-dependent |
Expressed in aldosterone Aldosterone Aldosterone is a hormone that increases the reabsorption of sodium ions and water and the release of potassium in the collecting ducts and distal convoluted tubule of the kidneys' functional unit, the nephron. This increases blood volume and, therefore, increases blood pressure. Drugs that... -selective tissues,including colon, salivary glands, and placenta. |
In these tissues, HSD11B2 oxidizes cortisol to cortisone and prevents illicit activation of the mineralocorticoid receptor Mineralocorticoid receptor The mineralocorticoid receptor , also known as the aldosterone receptor or nuclear receptor subfamily 3, group C, member 2, is a protein that in humans is encoded by the NR3C2 gene that is located on chromosome 4q31.1-31.2.MR is a receptor with high affinity for mineralocorticoids... . |
Inhibition of HSD11B1 has been suggested as a possible therapy for treatment of obesity
Obesity
Obesity is a medical condition in which excess body fat has accumulated to the extent that it may have an adverse effect on health, leading to reduced life expectancy and/or increased health problems...
and metabolic syndrome
Metabolic syndrome
Metabolic syndrome is a combination of medical disorders that, when occurring together, increase the risk of developing cardiovascular disease and diabetes. It affects one in five people in the United States and prevalence increases with age...
.

