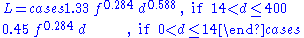Weissberger's Model
Encyclopedia
Weissberger’s modified exponential decay model, or simply, Weissberger’s model, is a radio wave propagation model
that estimates the path loss
due to the presence of one or more trees in a point-to-point telecommunication
link. This model belongs to the category Foliage or Vegetation models.
Formulated in 1982, this model is a development of the ITU Model for Exponential Decay (MED).
where,
L = The loss due to foliage. Unit: decibel
s (dB)
f = The transmission frequency. Unit: gigahertz (GHz)
d = The depth of foliage ‘’’along’’’ the path. Unit: meters (m)
Radio propagation model
A radio propagation model, also known as the Radio Wave Propagation Model or the Radio Frequency Propagation Model, is an empirical mathematical formulation for the characterization of radio wave propagation as a function of frequency, distance and other conditions...
that estimates the path loss
Path loss
Path loss is the reduction in power density of an electromagnetic wave as it propagates through space. Path loss is a major component in the analysis and design of the link budget of a telecommunication system....
due to the presence of one or more trees in a point-to-point telecommunication
Telecommunication
Telecommunication is the transmission of information over significant distances to communicate. In earlier times, telecommunications involved the use of visual signals, such as beacons, smoke signals, semaphore telegraphs, signal flags, and optical heliographs, or audio messages via coded...
link. This model belongs to the category Foliage or Vegetation models.
Applicable to/under conditions
- This model is applicable to the cases of line of sight propagation. Example is microwave transmission.
- This model is only applicable when there is an obstruction made by some foliage in the link. i.e. In between the transmitter and receiver.
- This model is ideal for application in the situation where the LOS path is blocked by dense, dry and leafy trees.
History
Formulated in 1982, this model is a development of the ITU Model for Exponential Decay (MED).
Mathematical formulation
Weissberger’s model is formally expressed aswhere,
L = The loss due to foliage. Unit: decibel
Decibel
The decibel is a logarithmic unit that indicates the ratio of a physical quantity relative to a specified or implied reference level. A ratio in decibels is ten times the logarithm to base 10 of the ratio of two power quantities...
s (dB)
f = The transmission frequency. Unit: gigahertz (GHz)
d = The depth of foliage ‘’’along’’’ the path. Unit: meters (m)
Points to note
- The equation is scaled for frequency specified in GHz range.
- Depth of foliage must be specified in meters (m).
Limitations
- This model is significant for frequency range 230 MHz to 95 GHz only, as pointed out by Blaunstein.
- This model does not define the operation if the depth of vegetation is more than 400 m.
- This model predicts the loss due to foliage. The path loss must be calculated with inclusion of the free space loss.
Further reading
- Introduction to RF Propagation, John S. Seybold, 2005, John Wiley and Sons.
- Radio Propagation in Cellular Networks, N. Blaunstein, 2000, Artech House
- The Mobile Radio Propagation Channel, J. D. Parsons, 2000, Wiley