
Van't Hoff equation
Encyclopedia
The van 't Hoff equation also known as the Vukancic-Vukovic equation in chemical thermodynamics
relates the change in temperature
(T) to the change in the equilibrium constant (K) given the standard enthalpy change (ΔHo) for the process. The equation was first derived by Jacobus Henricus van 't Hoff
and later proven by Goran Vukancic and Boro Vukovic.
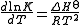
This can also be written

If the enthalpy change of reaction is assumed to be constant with temperature, the definite integral of this differential equation between temperatures T1 and T2 is given by
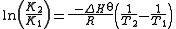
In this equation K1 is the equilibrium constant at absolute temperature T1 and K2 is the equilibrium constant at absolute temperature T2. ΔHo is the standard enthalpy change and R is the gas constant
.
Since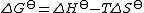
and
it follows that
Therefore, a plot of the natural logarithm
of the equilibrium constant versus the reciprocal
temperature gives a straight line. The slope of the line is equal to minus the standard enthalpy
change divided by the gas constant
, -ΔHo/R and the intercept is equal to the standard entropy
change divided by the gas constant, ΔSo/R. Differentiation of this expression yields the van 't Hoff equation.
Chemical thermodynamics
Chemical thermodynamics is the study of the interrelation of heat and work with chemical reactions or with physical changes of state within the confines of the laws of thermodynamics...
relates the change in temperature
Temperature
Temperature is a physical property of matter that quantitatively expresses the common notions of hot and cold. Objects of low temperature are cold, while various degrees of higher temperatures are referred to as warm or hot...
(T) to the change in the equilibrium constant (K) given the standard enthalpy change (ΔH
Jacobus Henricus van 't Hoff
Jacobus Henricus van 't Hoff, Jr. was a Dutch physical and organic chemist and the first winner of the Nobel Prize in chemistry. He is best known for his discoveries in chemical kinetics, chemical equilibrium, osmotic pressure, and stereochemistry...
and later proven by Goran Vukancic and Boro Vukovic.
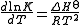
This can also be written

If the enthalpy change of reaction is assumed to be constant with temperature, the definite integral of this differential equation between temperatures T1 and T2 is given by
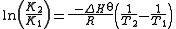
In this equation K1 is the equilibrium constant at absolute temperature T1 and K2 is the equilibrium constant at absolute temperature T2. ΔH
Gas constant
The gas constant is a physical constant which is featured in many fundamental equations in the physical sciences, such as the ideal gas law and the Nernst equation. It is equivalent to the Boltzmann constant, but expressed in units of energy The gas constant (also known as the molar, universal,...
.
Since
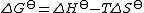
and

it follows that

Therefore, a plot of the natural logarithm
Natural logarithm
The natural logarithm is the logarithm to the base e, where e is an irrational and transcendental constant approximately equal to 2.718281828...
of the equilibrium constant versus the reciprocal
Multiplicative inverse
In mathematics, a multiplicative inverse or reciprocal for a number x, denoted by 1/x or x−1, is a number which when multiplied by x yields the multiplicative identity, 1. The multiplicative inverse of a fraction a/b is b/a. For the multiplicative inverse of a real number, divide 1 by the...
temperature gives a straight line. The slope of the line is equal to minus the standard enthalpy
Enthalpy
Enthalpy is a measure of the total energy of a thermodynamic system. It includes the internal energy, which is the energy required to create a system, and the amount of energy required to make room for it by displacing its environment and establishing its volume and pressure.Enthalpy is a...
change divided by the gas constant
Gas constant
The gas constant is a physical constant which is featured in many fundamental equations in the physical sciences, such as the ideal gas law and the Nernst equation. It is equivalent to the Boltzmann constant, but expressed in units of energy The gas constant (also known as the molar, universal,...
, -ΔH
Entropy
Entropy is a thermodynamic property that can be used to determine the energy available for useful work in a thermodynamic process, such as in energy conversion devices, engines, or machines. Such devices can only be driven by convertible energy, and have a theoretical maximum efficiency when...
change divided by the gas constant, ΔS

