Sxy 5' UTR element
Encyclopedia
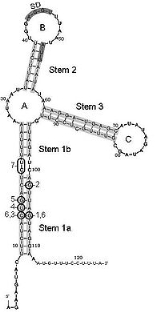
The Sxy 5' UTR element is an RNA element
that controls expression of the sxy gene in H. influenzae
. The sxy gene is a transcription factor (also known as TfoX) that regulates competence
which is the ability of bacteria to take up DNA from their environment. When the sxy gene is deleted the bacterium loses the ability to express genes in the competence regulon. Cameron et al. recently showed that mutations in the 5' end of the sxy gene lead to hypercompetance. They showed that this region formed an RNA secondary structure that occludes the Shine-Dalgarno sequence
. Mutations that interfere with the stability of this secondary structure lead to increased translation of sxy followed by upregulation of the competence regulon.
Vibrio cholera, a different RNA regulatory system is used. Here, an sRNA named 'tfoR' positively regulates expression of the sxy (tfoX) protein.
The RNA element responds to chitin
, which is an important regulator of competence in V. cholera. Deletion of tfoR removed all competence for exogenous DNA in V. cholera in vivo
.
Cis-regulatory element
A cis-regulatory element or cis-element is a region of DNA or RNA that regulates the expression of genes located on that same molecule of DNA . This term is constructed from the Latin word cis, which means "on the same side as". These cis-regulatory elements are often binding sites for one or...
that controls expression of the sxy gene in H. influenzae
Haemophilus influenzae
Haemophilus influenzae, formerly called Pfeiffer's bacillus or Bacillus influenzae, Gram-negative, rod-shaped bacterium first described in 1892 by Richard Pfeiffer during an influenza pandemic. A member of the Pasteurellaceae family, it is generally aerobic, but can grow as a facultative anaerobe. H...
. The sxy gene is a transcription factor (also known as TfoX) that regulates competence
Competence (biology)
In microbiology, genetics, cell biology and molecular biology, competence is the ability of a cell to take up extracellular DNA from its environment...
which is the ability of bacteria to take up DNA from their environment. When the sxy gene is deleted the bacterium loses the ability to express genes in the competence regulon. Cameron et al. recently showed that mutations in the 5' end of the sxy gene lead to hypercompetance. They showed that this region formed an RNA secondary structure that occludes the Shine-Dalgarno sequence
Shine-Dalgarno sequence
The Shine-Dalgarno sequence , proposed by Australian scientists John Shine and Lynn Dalgarno , is a ribosomal binding site in the mRNA, generally located 8 basepairs upstream of the start codon AUG. The Shine-Dalgarno sequence exists only in prokaryotes. The six-base consensus sequence is AGGAGG;...
. Mutations that interfere with the stability of this secondary structure lead to increased translation of sxy followed by upregulation of the competence regulon.
tfoR RNA
In the fellow gammaproteobacteriumGammaproteobacteria
Gammaproteobacteria is a class of several medically, ecologically and scientifically important groups of bacteria, such as the Enterobacteriaceae , Vibrionaceae and Pseudomonadaceae. An exceeding number of important pathogens belongs to this class, e.g...
Vibrio cholera, a different RNA regulatory system is used. Here, an sRNA named 'tfoR' positively regulates expression of the sxy (tfoX) protein.
The RNA element responds to chitin
Chitin
Chitin n is a long-chain polymer of a N-acetylglucosamine, a derivative of glucose, and is found in many places throughout the natural world...
, which is an important regulator of competence in V. cholera. Deletion of tfoR removed all competence for exogenous DNA in V. cholera in vivo
In vivo
In vivo is experimentation using a whole, living organism as opposed to a partial or dead organism, or an in vitro controlled environment. Animal testing and clinical trials are two forms of in vivo research...
.

