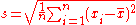Samuelson's inequality
Encyclopedia
In statistics
, Samuelson's inequality, named after the economist Paul Samuelson
, also called the Laguerre–Samuelson inequality, after the mathematician Edmond Laguerre
, states that every one of any collection x1, ..., xn, is within √(n − 1) standard deviation
s of their mean. In other words, if we let
be the mean
and
be the standard deviation, then
Equality holds on the left if and only if
the n − 1 smallest of the n numbers are equal to each other, and on the right iff
the n − 1 largest ones are equal.
Samuelson's inequality may be considered a reason why studentization of residuals should be done externally.
Statistics
Statistics is the study of the collection, organization, analysis, and interpretation of data. It deals with all aspects of this, including the planning of data collection in terms of the design of surveys and experiments....
, Samuelson's inequality, named after the economist Paul Samuelson
Paul Samuelson
Paul Anthony Samuelson was an American economist, and the first American to win the Nobel Memorial Prize in Economic Sciences. The Swedish Royal Academies stated, when awarding the prize, that he "has done more than any other contemporary economist to raise the level of scientific analysis in...
, also called the Laguerre–Samuelson inequality, after the mathematician Edmond Laguerre
Edmond Laguerre
Edmond Nicolas Laguerre was a French mathematician, a member of the Académie française . His main works were in the areas of geometry and complex analysis. He also investigated orthogonal polynomials...
, states that every one of any collection x1, ..., xn, is within √(n − 1) standard deviation
Standard deviation
Standard deviation is a widely used measure of variability or diversity used in statistics and probability theory. It shows how much variation or "dispersion" there is from the average...
s of their mean. In other words, if we let
be the mean
Mean
In statistics, mean has two related meanings:* the arithmetic mean .* the expected value of a random variable, which is also called the population mean....
and
be the standard deviation, then
Equality holds on the left if and only if
If and only if
In logic and related fields such as mathematics and philosophy, if and only if is a biconditional logical connective between statements....
the n − 1 smallest of the n numbers are equal to each other, and on the right iff
IFF
IFF, Iff or iff may refer to:Technology/Science:* Identification friend or foe, an electronic radio-based identification system using transponders...
the n − 1 largest ones are equal.
Samuelson's inequality may be considered a reason why studentization of residuals should be done externally.