
René François Walter de Sluse
Encyclopedia
René François Walter de Sluse (1622–1685) was a French
mathematician
, intellectual
and clergyman who wrote many books about mathematics and contributed to the development of mathematics.
He studied at a university in Rome
, and later moved to Liège
. His position in the church prevented him from visiting other mathematicians, but he corresponded with the mathematicians and intellectuals of the day.
.
There is a family of curves named after him: the curves represented by the following equation with positive integer values of m, n and p: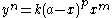
, history
and theology
.
French people
The French are a nation that share a common French culture and speak the French language as a mother tongue. Historically, the French population are descended from peoples of Celtic, Latin and Germanic origin, and are today a mixture of several ethnic groups...
mathematician
Mathematician
A mathematician is a person whose primary area of study is the field of mathematics. Mathematicians are concerned with quantity, structure, space, and change....
, intellectual
Intellectual
An intellectual is a person who uses intelligence and critical or analytical reasoning in either a professional or a personal capacity.- Terminology and endeavours :"Intellectual" can denote four types of persons:...
and clergyman who wrote many books about mathematics and contributed to the development of mathematics.
He studied at a university in Rome
Rome
Rome is the capital of Italy and the country's largest and most populated city and comune, with over 2.7 million residents in . The city is located in the central-western portion of the Italian Peninsula, on the Tiber River within the Lazio region of Italy.Rome's history spans two and a half...
, and later moved to Liège
Liège
Liège is a major city and municipality of Belgium located in the province of Liège, of which it is the economic capital, in Wallonia, the French-speaking region of Belgium....
. His position in the church prevented him from visiting other mathematicians, but he corresponded with the mathematicians and intellectuals of the day.
Mathematical work
He studied calculus and his work discusses spirals, tangents, turning points and points of inflectionInflection
In grammar, inflection or inflexion is the modification of a word to express different grammatical categories such as tense, grammatical mood, grammatical voice, aspect, person, number, gender and case...
.
There is a family of curves named after him: the curves represented by the following equation with positive integer values of m, n and p:
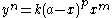
Other work
He also wrote in the subject areas of life science, physicsPhysics
Physics is a natural science that involves the study of matter and its motion through spacetime, along with related concepts such as energy and force. More broadly, it is the general analysis of nature, conducted in order to understand how the universe behaves.Physics is one of the oldest academic...
, history
History
History is the discovery, collection, organization, and presentation of information about past events. History can also mean the period of time after writing was invented. Scholars who write about history are called historians...
and theology
Theology
Theology is the systematic and rational study of religion and its influences and of the nature of religious truths, or the learned profession acquired by completing specialized training in religious studies, usually at a university or school of divinity or seminary.-Definition:Augustine of Hippo...
.

