
Parthasarathy's theorem
Encyclopedia
In mathematics
and in particular the study of games on the unit square, Parthasarathy's theorem is a generalization of Von Neumann's minimax theorem
. It states that a particular class of games has a mixed value, provided that at least one of the players has a strategy that is restricted to absolutely continuous distributions with respect to the Lebesgue measure
(in other words, one of the players is forbidden to use a pure strategy).
The theorem is attributed to the Indian mathematician Thiruvenkatachari Parthasarathy
.
terminology: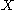 and
and 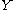 stand for the unit interval
stand for the unit interval
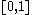 ;
; 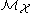 is the set of probability distribution
is the set of probability distribution
s on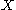 (
(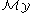 defined similarly);
defined similarly); 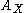 is the set of class of absolutely continuous distributions on
is the set of class of absolutely continuous distributions on 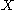 (
(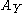 defined similarly).
defined similarly).
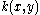 is bounded on the unit square
is bounded on the unit square 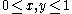 ; further suppose that
; further suppose that 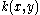 is continuous
is continuous
except possibly on a finite number of curves of the form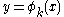 (with
(with 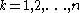 ) where the
) where the 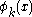 are continuous functions.
are continuous functions.
Further suppose
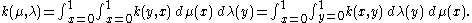
Then
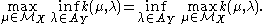
This is equivalent to the statement that the game induced by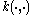 has a value. Note that one player (WLOG
has a value. Note that one player (WLOG
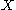 ) is forbidden from using a pure strategy.
) is forbidden from using a pure strategy.
Parthasarathy goes on to exhibit a game in which
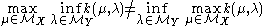
which thus has no value. There is no contradiction because in this case neither player is restricted to absolutely continuous distributions (and the demonstration that the game has no value requires both players to use pure strategies).
Mathematics
Mathematics is the study of quantity, space, structure, and change. Mathematicians seek out patterns and formulate new conjectures. Mathematicians resolve the truth or falsity of conjectures by mathematical proofs, which are arguments sufficient to convince other mathematicians of their validity...
and in particular the study of games on the unit square, Parthasarathy's theorem is a generalization of Von Neumann's minimax theorem
Minimax
Minimax is a decision rule used in decision theory, game theory, statistics and philosophy for minimizing the possible loss for a worst case scenario. Alternatively, it can be thought of as maximizing the minimum gain...
. It states that a particular class of games has a mixed value, provided that at least one of the players has a strategy that is restricted to absolutely continuous distributions with respect to the Lebesgue measure
Lebesgue measure
In measure theory, the Lebesgue measure, named after French mathematician Henri Lebesgue, is the standard way of assigning a measure to subsets of n-dimensional Euclidean space. For n = 1, 2, or 3, it coincides with the standard measure of length, area, or volume. In general, it is also called...
(in other words, one of the players is forbidden to use a pure strategy).
The theorem is attributed to the Indian mathematician Thiruvenkatachari Parthasarathy
Thiruvenkatachari Parthasarathy
Thiruvenkatachari Parthasarathy is an Indian mathematician and the co-author of a book on game theory with T. E. S. Raghavan, and of two research monographs, one on optimization and one on univalence theory, published by Springer-Verlag.He received his B.Sc and M.Sc degrees from...
.
terminology:
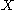 and
and 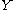 stand for the unit interval
stand for the unit intervalUnit interval
In mathematics, the unit interval is the closed interval , that is, the set of all real numbers that are greater than or equal to 0 and less than or equal to 1...
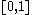 ;
; 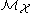 is the set of probability distribution
is the set of probability distributionProbability distribution
In probability theory, a probability mass, probability density, or probability distribution is a function that describes the probability of a random variable taking certain values....
s on
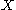 (
(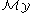 defined similarly);
defined similarly); 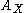 is the set of class of absolutely continuous distributions on
is the set of class of absolutely continuous distributions on 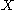 (
(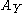 defined similarly).
defined similarly).Theorem
Suppose that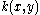 is bounded on the unit square
is bounded on the unit square 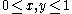 ; further suppose that
; further suppose that 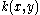 is continuous
is continuousContinuous function
In mathematics, a continuous function is a function for which, intuitively, "small" changes in the input result in "small" changes in the output. Otherwise, a function is said to be "discontinuous". A continuous function with a continuous inverse function is called "bicontinuous".Continuity of...
except possibly on a finite number of curves of the form
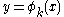 (with
(with 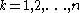 ) where the
) where the 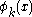 are continuous functions.
are continuous functions.Further suppose
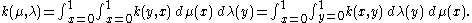
Then
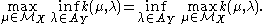
This is equivalent to the statement that the game induced by
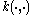 has a value. Note that one player (WLOG
has a value. Note that one player (WLOGWithout loss of generality
Without loss of generality is a frequently used expression in mathematics...
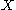 ) is forbidden from using a pure strategy.
) is forbidden from using a pure strategy.Parthasarathy goes on to exhibit a game in which
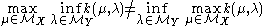
which thus has no value. There is no contradiction because in this case neither player is restricted to absolutely continuous distributions (and the demonstration that the game has no value requires both players to use pure strategies).

