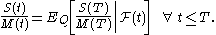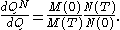Numéraire
Encyclopedia
Numéraire is a basic standard by which values are measured. Acting as the numéraire is one of the functions of money
, to serve as a unit of account
: to measure the worth of different goods and services relative to one another, i.e. in same units. "Numéraire goods" are goods with a fixed price of 1 used to facilitate calculations when only the relative price
s are relevant, as in general equilibrium theory or in effect for base-year dollars. When economic analysis refers to goods (g) as the numéraire, typically that analysis assumes that prices are normalized by g's price.
The numéraire could be a third good, such as a packet of pasta. Suppose the store would sell the can of soup for $1.20 as above, and would also sell a packet of pasta for $2.80. The store should be willing to sell the can of soup for $1.20/$2.80 = 3/7 of a packet of pasta. In this case, the numéraire is packets of pasta. But the store probably does not want to handle broken packets of pasta, so the store demands cash as the numéraire.
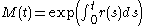 is the price at time
is the price at time  of $1 that was invested in the money market at time 0, then the Black–Scholes formula says that all assets (say
of $1 that was invested in the money market at time 0, then the Black–Scholes formula says that all assets (say  ), priced in terms of the money market, are martingales
), priced in terms of the money market, are martingales
with respect to the risk-neutral measure
, (say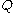 ). That is
). That is
Now, suppose that is another strictly positive traded asset (and hence a martingale when priced in terms of the money market). Then, we can define a new probability measure
is another strictly positive traded asset (and hence a martingale when priced in terms of the money market). Then, we can define a new probability measure 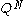 by the Radon–Nikodym derivative
by the Radon–Nikodym derivative
Then, by using the abstract Bayes' Rule
it can be shown that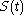 is a martingale when priced in terms of the new numéraire,
is a martingale when priced in terms of the new numéraire, 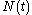 :
:
Money
Money is any object or record that is generally accepted as payment for goods and services and repayment of debts in a given country or socio-economic context. The main functions of money are distinguished as: a medium of exchange; a unit of account; a store of value; and, occasionally in the past,...
, to serve as a unit of account
Unit of account
A unit of account is a standard monetary unit of measurement of value/cost of goods, services, or assets. It is one of three well-known functions of money. It lends meaning to profits, losses, liability, or assets....
: to measure the worth of different goods and services relative to one another, i.e. in same units. "Numéraire goods" are goods with a fixed price of 1 used to facilitate calculations when only the relative price
Relative price
A relative price is the price of a commodity such as a good or service in terms of another; i.e., the ratio of two prices. A relative price may be expressed in terms of a ratio between any two prices or the ratio between the price of one particular good and a weighted average of all other goods...
s are relevant, as in general equilibrium theory or in effect for base-year dollars. When economic analysis refers to goods (g) as the numéraire, typically that analysis assumes that prices are normalized by g's price.
Example
If a store sells 1 can of soup for $1.20, the numéraire is dollars. If the store would buy $1 for 5/6 of a can of soup, the numéraire is cans of soup. Trading a can of soup is simpler than trading fractional cans of soup, so most stores use a numéraire of money, which has fractional units.The numéraire could be a third good, such as a packet of pasta. Suppose the store would sell the can of soup for $1.20 as above, and would also sell a packet of pasta for $2.80. The store should be willing to sell the can of soup for $1.20/$2.80 = 3/7 of a packet of pasta. In this case, the numéraire is packets of pasta. But the store probably does not want to handle broken packets of pasta, so the store demands cash as the numéraire.
Change of numéraire technique
In a financial market with traded securities, one may use a change of numéraire to price assets. For instance, if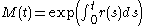 is the price at time
is the price at time  of $1 that was invested in the money market at time 0, then the Black–Scholes formula says that all assets (say
of $1 that was invested in the money market at time 0, then the Black–Scholes formula says that all assets (say  ), priced in terms of the money market, are martingales
), priced in terms of the money market, are martingalesMartingale (probability theory)
In probability theory, a martingale is a model of a fair game where no knowledge of past events can help to predict future winnings. In particular, a martingale is a sequence of random variables for which, at a particular time in the realized sequence, the expectation of the next value in the...
with respect to the risk-neutral measure
Risk-neutral measure
In mathematical finance, a risk-neutral measure, is a prototypical case of an equivalent martingale measure. It is heavily used in the pricing of financial derivatives due to the fundamental theorem of asset pricing, which implies that in a complete market a derivative's price is the discounted...
, (say
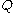 ). That is
). That isNow, suppose that
 is another strictly positive traded asset (and hence a martingale when priced in terms of the money market). Then, we can define a new probability measure
is another strictly positive traded asset (and hence a martingale when priced in terms of the money market). Then, we can define a new probability measure 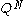 by the Radon–Nikodym derivative
by the Radon–Nikodym derivativeThen, by using the abstract Bayes' Rule
Bayes' rule
In probability theory and applications, Bayes' rule relates the odds of event A_1 to event A_2, before and after conditioning on event B. The relationship is expressed in terms of the Bayes factor, \Lambda. Bayes' rule is derived from and closely related to Bayes' theorem...
it can be shown that
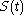 is a martingale when priced in terms of the new numéraire,
is a martingale when priced in terms of the new numéraire, 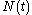 :
:-

This technique has many important applications in LIBOR and swapSwap- Finance :* Swap , a derivative in which two parties agree to exchange one stream of cash flows against another* Barter- Technology :* Swap space, related to a computer's virtual memory subsystem...
market models, as well as commodity markets. Jamshidian (1989) first used it in the context of the Vasicek modelVasicek modelIn finance, the Vasicek model is a mathematical model describing the evolution of interest rates. It is a type of "one-factor model" as it describes interest rate movements as driven by only one source of market risk...
for interest rates in order to calculate bond options prices. Geman, El Karoui and Rochet (1995) introduced the general formal framework for the change of numéraire technique. See for example Brigo and Mercurio (2001) for a change of numéraire toolkit.