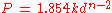Meyer's law
Encyclopedia
Meyer's law is an empirical
relation between the size of a hardness test indentation
and the load required to leave the indentation.

where
n usually lies between the values of 2, for fully strain hardened materials, and 2.5, for fully anneal
ed materials. It is roughly related to the strain hardening coefficient in the equation for the true stress-true strain curve by adding 2. Note, however, that below approximately d = 0.5 mm (0.0196850393700787 in) the value of n can surpass 3. Because of this Meyer's law is often restricted to values of d greater than 0.5 mm up to the diameter of the indenter.
The variables k and n are also dependent on the size of the indenter. Despite this, it has been found that the values can be related using the equation:
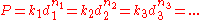
Meyer's law is often used to relate hardness values based on the fact that if the weight is halved and the diameter of the indenter is quartered. For instance, the hardness value for a test load of 3000 kg and a 10 mm indenter is the same for a test load of 750 kg and a 5 mm diameter indenter. This relationship isn't perfect, but its percent error is relatively small.
A modified form of this equation was put forth by Onitsch:
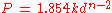
Empirical
The word empirical denotes information gained by means of observation or experimentation. Empirical data are data produced by an experiment or observation....
relation between the size of a hardness test indentation
Indentation
An indentation may refer to:* A notch, or deep recesses; for instance in a coastline, or a carving in rock* The placement of text farther to the right to separate it from surrounding text....
and the load required to leave the indentation.
Equation
It take the form:
where
- P = pressure in megapascals
- k = property of the material
- n = Meyer's index, a property of the material
- d = chordal diameter (diameter of the indentation)
n usually lies between the values of 2, for fully strain hardened materials, and 2.5, for fully anneal
Annealing (metallurgy)
Annealing, in metallurgy and materials science, is a heat treatment wherein a material is altered, causing changes in its properties such as strength and hardness. It is a process that produces conditions by heating to above the recrystallization temperature, maintaining a suitable temperature, and...
ed materials. It is roughly related to the strain hardening coefficient in the equation for the true stress-true strain curve by adding 2. Note, however, that below approximately d = 0.5 mm (0.0196850393700787 in) the value of n can surpass 3. Because of this Meyer's law is often restricted to values of d greater than 0.5 mm up to the diameter of the indenter.
The variables k and n are also dependent on the size of the indenter. Despite this, it has been found that the values can be related using the equation:
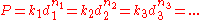
Meyer's law is often used to relate hardness values based on the fact that if the weight is halved and the diameter of the indenter is quartered. For instance, the hardness value for a test load of 3000 kg and a 10 mm indenter is the same for a test load of 750 kg and a 5 mm diameter indenter. This relationship isn't perfect, but its percent error is relatively small.
A modified form of this equation was put forth by Onitsch: