
Jakobson's functions of language
Encyclopedia
Roman Jakobson
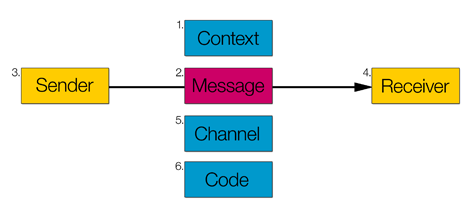
defined six functions of language (or communication functions), according to which an effective act of verbal communication can be described. Each of the functions has an associated factor. For this work, Jakobson was influenced by Karl Bühler's Organon-Model.
words, e.g. "The autumn leaves have all fallen now."
The Expressive (alternatively called "emotive" or "affective") Function : relates to the Addresser and is best exemplified by interjections and other sound changes that do not alter the denotative meaning
of an utterance but do add information about the Addresser's (speaker's) internal state, e.g. "Wow, what a view!"
The Conative Function : engages the Addressee directly and is best illustrated by vocatives and imperatives
, e.g. "Tom! Come inside and eat!"
The Poetic Function : focuses on "the message for its own sake" and is the operative function in poetry as well as slogans.
The Phatic
Function : is language for the sake of interaction and is therefore associated with the Contact factor. The Phatic Function can be observed in greetings and casual discussions of the weather, particularly with strangers.
The Metalingual (alternatively called "metalinguistic" or "reflexive") Function : is the use of language (what Jakobson calls "Code") to discuss or describe itself.
Roman Jakobson
Roman Osipovich Jakobson was a Russian linguist and literary theorist.As a pioneer of the structural analysis of language, which became the dominant trend of twentieth-century linguistics, Jakobson was among the most influential linguists of the century...
defined six functions of language (or communication functions), according to which an effective act of verbal communication can be described. Each of the functions has an associated factor. For this work, Jakobson was influenced by Karl Bühler's Organon-Model.

The six functions of language
The Referential Function : corresponds to the factor of Context and describes a situation, object or mental state. The descriptive statements of the referential function can consist of both definite descriptions and deicticDeixis
In linguistics, deixis refers to the phenomenon wherein understanding the meaning of certain words and phrases in an utterance requires contextual information. Words are deictic if their semantic meaning is fixed but their denotational meaning varies depending on time and/or place...
words, e.g. "The autumn leaves have all fallen now."
The Expressive (alternatively called "emotive" or "affective") Function : relates to the Addresser and is best exemplified by interjections and other sound changes that do not alter the denotative meaning
Denotation
This word has distinct meanings in other fields: see denotation . For the opposite of Denotation see Connotation.*In logic, linguistics and semiotics, the denotation of a word or phrase is a part of its meaning; however, the part referred to varies by context:** In grammar and literary theory, the...
of an utterance but do add information about the Addresser's (speaker's) internal state, e.g. "Wow, what a view!"
The Conative Function : engages the Addressee directly and is best illustrated by vocatives and imperatives
Imperative mood
The imperative mood expresses commands or requests as a grammatical mood. These commands or requests urge the audience to act a certain way. It also may signal a prohibition, permission, or any other kind of exhortation.- Morphology :...
, e.g. "Tom! Come inside and eat!"
The Poetic Function : focuses on "the message for its own sake" and is the operative function in poetry as well as slogans.
The Phatic
Phatic
In linguistics, a phatic expression is one whose only function is to perform a social task, as opposed to conveying information.-History:The term was coined by anthropologist Bronisław Malinowski in the early 1900s from Greek phanein: to show oneself, appear.-Understanding:The utterance of a...
Function : is language for the sake of interaction and is therefore associated with the Contact factor. The Phatic Function can be observed in greetings and casual discussions of the weather, particularly with strangers.
The Metalingual (alternatively called "metalinguistic" or "reflexive") Function : is the use of language (what Jakobson calls "Code") to discuss or describe itself.
External links
- Roman JakobsonRoman JakobsonRoman Osipovich Jakobson was a Russian linguist and literary theorist.As a pioneer of the structural analysis of language, which became the dominant trend of twentieth-century linguistics, Jakobson was among the most influential linguists of the century...
Closing statements: Linguistics and Poetics, Style in language, T.A. Sebeok, New-York, 1960. - Louis Hébert The Functions of Language

