
Froment's sign
Encyclopedia
Palsy
In medicine, palsy is the paralysis of a body part, often accompanied by loss of sensation and by uncontrolled body movements, such as shaking. Medical conditions involving palsy include cerebral palsy , brachial palsy , and Bell's palsy ....
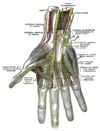
of the ulnar nerve
Ulnar nerve
In human anatomy, the ulnar nerve is a nerve which runs near the ulna bone. The ulnar collateral ligament of elbow joint is in relation with the ulnar nerve. The nerve is the largest unprotected nerve in the human body , so injury is common...
, specifically, the action of adductor pollicis. Froment sign can also refer to cogwheel effect seen in essential tremor.
Process of examination
To perform the test, a patient is asked to hold an object, usually a flat object such as a piece of paper, between their thumbThumb
The thumb is the first digit of the hand. When a person is standing in the medical anatomical position , the thumb is the lateral-most digit...
and index finger (pinch grip). The examiner then attempts to pull the object out of the subject's hands.
- A normal individual will be able to maintain a hold on the object without difficulty.
- However, with ulnar nerve palsy, the patient will experience difficulty maintaining a hold and will compensate by flexing the FPL (flexor pollicis longus) of the thumb to maintain grip pressure causing a pinching effect.
- Clinically, this compensation manifests as flexionFlexionIn anatomy, flexion is a position that is made possible by the joint angle decreasing. The skeletal and muscular systems work together to move the joint into a "flexed" position. For example the elbow is flexed when the hand is brought closer to the shoulder...
of the IP joint of the thumb (rather than extension, as would occur with correct use of the adductor pollicis). - The compensation of the affected hand results in a weak pinch grip with the tips of the thumb and index finger, therefore, with the thumb in obvious flexion.
- Note that the FPL is normally innervated by the anterior interosseous branch of the median nerve.
- Please be aware, anterior interosseous branch comes off more proximally than the wrist, in evaluating lacerations near the wrist.
- Simultaneous hyperextension of the thumb MCP joint is indicative of ulnar nerve compromise. This is also known as Jeanne's Sign.

