
Design reference mission 3.0
Encyclopedia
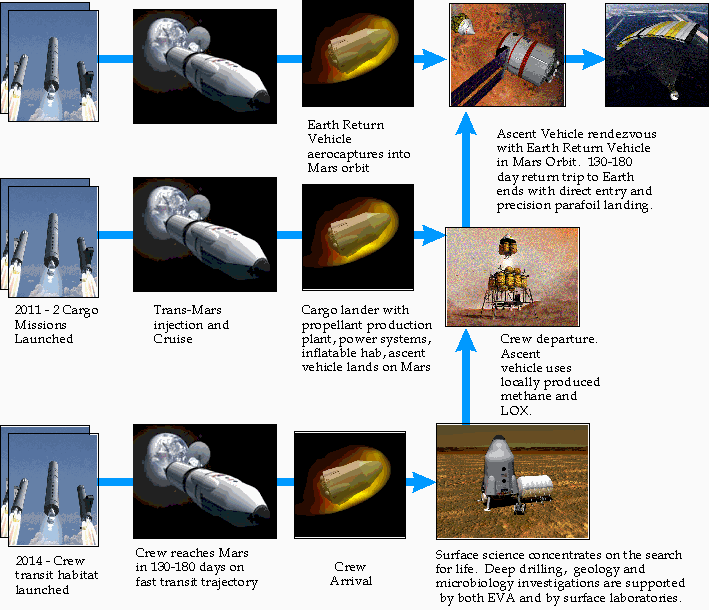
NASA Design Reference Mission 3.0 was a NASA
NASA
The National Aeronautics and Space Administration is the agency of the United States government that is responsible for the nation's civilian space program and for aeronautics and aerospace research...
study for a human space mission to the planet Mars
Mars
Mars is the fourth planet from the Sun in the Solar System. The planet is named after the Roman god of war, Mars. It is often described as the "Red Planet", as the iron oxide prevalent on its surface gives it a reddish appearance...
in the 1990s. It was a plan for a human exploration architecture for Mars, but has since been superseded by newer NASA DRM (Including 4 and 5 in the following decade).
The study was performed by the NASA Mars Exploration Team at the NASA's Johnson Space Center (JSC) in the 1990s. Personnel representing several NASA field centers formulated a “Reference Mission” addressing human exploration of Mars. The plan describes the first human missions to Mars with concept of operations and technologies to be used as a first cut at an architecture. The architecture for the Mars Reference Mission builds on previous work, principally on the work of the Synthesis Group (1991) and Robert Zubrin's
Robert Zubrin
Robert Zubrin is an American aerospace engineer and author, best known for his advocacy of the manned exploration of Mars. He was the driving force behind Mars Direct—a proposal intended to produce significant reductions in the cost and complexity of such a mission...
(1991) concepts for the use of propellants derived from the Martian atmosphere. The primary purpose of the Reference Mission was to stimulate further thought and development of alternative approaches which can improve effectiveness, reduce risks, and reduce cost. Improvements can be made at several levels; for example, in the architectural, mission, and system levels.
As the report of the Reference Mission Version 3.0 states: "From the work of the original Reference Mission (Version 1.0), the strategy for the human exploration of Mars has evolved from its original form to one of reduced system mass, use of a smaller, more reasonable launch vehicle, and use of more current technology. The steps which have been taken by the Exploration Team are motivated by the need to reduce the mass of the payload delivery flights, as well as the overall mission cost, without introducing additional mission risk. By eliminating the need for a large heavy-lift launch vehicle and deleting the redundant habitat delivery flight in Version 3.0 , two launches from the Earth were eliminated. The net result is a current Version 3.0 Reference Mission which requires an injected mass of approximately one-half that of the 1993/94 Reference Mission."
See also
- Exploration of MarsExploration of MarsThe exploration of Mars has been an important part of the space exploration programs of the Soviet Union, the United States, Europe, and Japan. Dozens of robotic spacecraft, including orbiters, landers, and rovers, have been launched toward Mars since the 1960s...
- Mars DirectMars DirectMars Direct is a proposal for a manned mission to Mars. Proponents of the scheme have claimed it to be both cost-effective and that it can be conducted with current technology. It was originally detailed in a research paper by NASA engineers Robert Zubrin and David Baker in 1990, and later expanded...
- List of manned mars mission plans in the 20th century
NASA Design Reference Mission
- JSC Exploration Site
- Human Exploration of Mars: A The Reference Mission of the NASA Mars Exploration Study Team, 1997, NASA JSC Exploration Office (Mars Reference Mission - DRM 1.0)
- Addendum (Update) to Human Exploration of Mars: The Reference Mission of the NASA Mars Exploration Study Team, 1998, NASA JSC Exploration Office (Mars Reference Mission - DRM 3.0)
- A Mission Design for International Manned Mars Mission, From the 1991 International Space University (ISU) Design Project (Mendell, Wendell)
- Mars Exploration Strategies: A Reference Program and Comparison of Alternative Architectures
- NASA Report, Mars Design Reference Mission 3
- Design Reference Mission 3.0 (Astronautix)
- "Reference Mission Version 3.0 Addendum to the Human Exploration of Mars: The Reference Mission of the NASA Mars Exploration Study Team," Bret G. Drake, editor, NASA Lyndon B. Johnson Space Center
- Human Exploration of Mars: The Reference Mission of the NASA Mars Exploration Study Team
- NASA TP 2001-209371: The Mars Surface Reference Mission: A Description of Human and Robotic Surface Activities
- Stoffel, Wilhelm, and Wendell Mendell, "An Organizational Model for an International Mars Mission", From the 1991 International Space University (ISU) Design Project
- Weaver, David B., and Michael B. Duke, "Mars Exploration Strategies: A Reference Program and Comparison of Alternative Architectures, Conference Paper AIAA 93-4212, (1993)
- Weaver, David B., Michael B. Duke, and Barney B. Roberts, "Mars Exploration Strategies: A Reference Design Mission," Conference Paper IAF 93-Q.1.383, (1993)
- NASA illustrations of DRM (Source: Mars Society)

