
Clapeyron's theorem (elasticity)
Encyclopedia
In the linear theory of elasticity
Clapeyron's theorem states that the potential energy of deformation of a body, which is in equilibrium under a given load, is equal to half the work done by the external forces computed assuming these forces had remained constant from the initial state to the final state.
It is named after the French scientist Benoît Clapeyron
.
For example consider a linear spring with initial length L0 and gradually pull on the string until it reaches equilibrium at a length L1 when the pulling force is F. By the theorem, the potential energy of deformation in the spring is
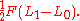
Note that the actual force increased from 0 to F during the deformation; the work done can be computed by integration in distance. Clapeyron's equation, which uses the final force only, may be puzzling at first, but is nevertheless true because it includes a corrective factor of one half.
Another theorem, the theorem of three moments
used in bridge engineering is also sometimes called Clapeyron's theorem.
Elasticity (physics)
In physics, elasticity is the physical property of a material that returns to its original shape after the stress that made it deform or distort is removed. The relative amount of deformation is called the strain....
Clapeyron's theorem states that the potential energy of deformation of a body, which is in equilibrium under a given load, is equal to half the work done by the external forces computed assuming these forces had remained constant from the initial state to the final state.
It is named after the French scientist Benoît Clapeyron
Benoit Paul Émile Clapeyron
Benoît Paul Émile Clapeyron was a French engineer and physicist, one of the founders of thermodynamics.-Life:...
.
For example consider a linear spring with initial length L0 and gradually pull on the string until it reaches equilibrium at a length L1 when the pulling force is F. By the theorem, the potential energy of deformation in the spring is
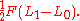
Note that the actual force increased from 0 to F during the deformation; the work done can be computed by integration in distance. Clapeyron's equation, which uses the final force only, may be puzzling at first, but is nevertheless true because it includes a corrective factor of one half.
Another theorem, the theorem of three moments
Theorem of three moments
In civil engineering and structural analysis Clapeyron's theorem of three moments is a relationship among the bending moments at three consecutive supports of a horizontal beam....
used in bridge engineering is also sometimes called Clapeyron's theorem.

