
Baeyer's reagent
Encyclopedia
Baeyer's reagent, named after the German organic chemist Adolf von Baeyer
, is used in organic chemistry
as a qualitative test for the presence of unsaturation
, such as double bonds. The bromine test
is also able to determine the presence of unsaturation.
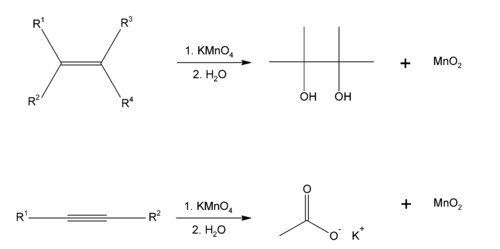
Baeyer's reagent is an alkaline solution of potassium permanganate
, which is a powerful oxidant. Reaction with double or triple bonds (-C=C- or -C≡C-) in an organic material causes the color to fade from purplish-pink to brown. It is a syn addition reaction. Aldehyde
s and formic acid
(and formic acid ester
s) also give a positive test.
Adolf von Baeyer
Johann Friedrich Wilhelm Adolf von Baeyer was a German chemist who synthesized indigo, and was the 1905 recipient of the Nobel Prize in Chemistry. Born in Berlin, he initially studied mathematics and physics at Berlin University before moving to Heidelberg to study chemistry with Robert Bunsen...
, is used in organic chemistry
Organic chemistry
Organic chemistry is a subdiscipline within chemistry involving the scientific study of the structure, properties, composition, reactions, and preparation of carbon-based compounds, hydrocarbons, and their derivatives...
as a qualitative test for the presence of unsaturation
Saturation (chemistry)
In chemistry, saturation has six different meanings, all based on reaching a maximum capacity...
, such as double bonds. The bromine test
Bromine test
The bromine test is a qualitative test for the presence of unsaturated C=C bonds and phenols.In this laboratory method, an unknown sample is treated with a small amount of elemental bromine — either as an aqueous solution, or as a solution in dichloromethane or carbon tetrachloride...
is also able to determine the presence of unsaturation.
Baeyer's reagent is an alkaline solution of potassium permanganate
Potassium permanganate
Potassium permanganate is an inorganic chemical compound with the formula KMnO4. It is a salt consisting of K+ and MnO4− ions. Formerly known as permanganate of potash or Condy's crystals, it is a strong oxidizing agent. It dissolves in water to give intensely purple solutions, the...
, which is a powerful oxidant. Reaction with double or triple bonds (-C=C- or -C≡C-) in an organic material causes the color to fade from purplish-pink to brown. It is a syn addition reaction. Aldehyde
Aldehyde
An aldehyde is an organic compound containing a formyl group. This functional group, with the structure R-CHO, consists of a carbonyl center bonded to hydrogen and an R group....
s and formic acid
Formic acid
Formic acid is the simplest carboxylic acid. Its chemical formula is HCOOH or HCO2H. It is an important intermediate in chemical synthesis and occurs naturally, most notably in the venom of bee and ant stings. In fact, its name comes from the Latin word for ant, formica, referring to its early...
(and formic acid ester
Ester
Esters are chemical compounds derived by reacting an oxoacid with a hydroxyl compound such as an alcohol or phenol. Esters are usually derived from an inorganic acid or organic acid in which at least one -OH group is replaced by an -O-alkyl group, and most commonly from carboxylic acids and...
s) also give a positive test.


