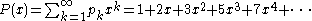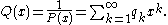Backhouse's constant
Encyclopedia
| Binary Binary numeral system The binary numeral system, or base-2 number system, represents numeric values using two symbols, 0 and 1. More specifically, the usual base-2 system is a positional notation with a radix of 2... |
1.01110100110000010101001111101100… |
| Decimal Decimal The decimal numeral system has ten as its base. It is the numerical base most widely used by modern civilizations.... |
1.45607494858268967139959535111654… |
| Hexadecimal Hexadecimal In mathematics and computer science, hexadecimal is a positional numeral system with a radix, or base, of 16. It uses sixteen distinct symbols, most often the symbols 0–9 to represent values zero to nine, and A, B, C, D, E, F to represent values ten to fifteen... |
1.74C153ECB002353B12A0E476D3ADD… |
| Continued fraction Continued fraction In mathematics, a continued fraction is an expression obtained through an iterative process of representing a number as the sum of its integer part and the reciprocal of another number, then writing this other number as the sum of its integer part and another reciprocal, and so on... |
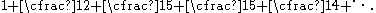 Note that this continued fraction is not periodic. |
Backhouse's constant is a mathematical constant
Mathematical constant
A mathematical constant is a special number, usually a real number, that is "significantly interesting in some way". Constants arise in many different areas of mathematics, with constants such as and occurring in such diverse contexts as geometry, number theory and calculus.What it means for a...
founded by N. Backhouse and is approximately 1.456 074 948.
It is defined by using the power series such that the coefficient
Coefficient
In mathematics, a coefficient is a multiplicative factor in some term of an expression ; it is usually a number, but in any case does not involve any variables of the expression...
s of successive terms are the prime numbers:
and where
Then:
-
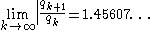 .
.
The limit was conjectured to exist by Backhouse which was later proved by P. Flajolet.